
Uncompromising speed, infinite flexibility


High performance
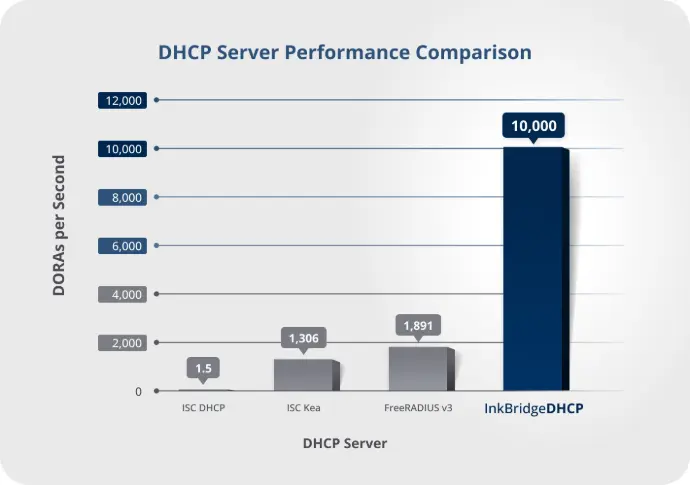
By leveraging the advanced multi-threaded capabilities of our platform, our DHCP server achieves enviable DORA rates of 10,000 per second per CPU core. That's almost ten times faster than the competition.
High availability
Our products are designed to work seamlessly in multi-system configurations with high availability (HA), or load balancing. These configurations allow it to handle wide fluctuations in loads in demanding environments, while not compromising on our best-in-class performance and stability.
Supports DHCPv4 and DHCPv6
We believe that customers should be able to use the DHCP version that is the best fit for their unique business needs. Our DHCP server is fully featured for both DHCPv4 and DHCPv6.
Easily scalable
Your network requirements today are not the same as your network requirements two years from now. InkBridgeDHCP is designed to grow with your business. Adding additional servers is easy, and allows you to linearly scale the capacity of the DHCP service as needed.
The world's fastest DHCP server
Saying that we've created the world's fastest DHCP server is a bold claim, but we are prepared to back it up with test data.
In our performance testing, InkBridgeDHCP performed almost ten times faster than competing DHCP servers. We achieve this impressive performance by leveraging the advanced multi-threaded capabilities of our platform, and combining it with the speed enhancements of modern key-value databases.
The end result is a DORA rate of 10,000 DORAs per second per CPU core. This is a performance profile which dramatically outpaces what other DHCP servers can offer.
Who We’ve Helped








![]()
Standards supported
We have full support for all DHCPv4 and DHCPv6 standards.
- From RFC 2131 to RFC 8925, all of DHCPv4 is supported
- From RFC 3315 to RFC 8357, all of DHCPv6 is supported.
Performance is, of course, a priority. Depending on the database, it is possible to get 10,000 DORAs per second on commodity hardware.
![]()
Compatible databases
InkBridgeDHCP is completely database agnostic. If you already have database infrastructure, we can work with it, including:
- MySQL
- Active Directory
- Azure AD / Entra ID
- Open LDAP
- PostgreSQL
- Redis
- Oracle
- Microsoft SQL Server
- MongoDB
- IBM DB2
Additional lease allocation options
In addition to databases, InkBridgeDHCP can work with every conceivable storage option:
- Cassandra
- Any custom REST API
- Any cloud based datastore such as Couchbase
Looking for FreeRADIUS support instead?
Never get stuck in low level support purgatory again.
Get rapid responses, direct from the people who wrote FreeRADIUS, and many of the RADIUS standards.
Resilient by design
We understand that in our unpredictable world, a site can go down because of extreme weather events, problems with the local power grid, or even human error.
InkBridgeDHCP supports multi-site replication, so that when an IP address is allocated, the record is copied asynchronously to another location. This duplication ensures network resilience in the event of a site failure. There is always a backup that holds the lease allocation, ensuring that the IP addresses remain consistent even when the issuing site is unavailable.
Performance unaffected by address pool capacity
IT system administrators no longer need to wrestle with balancing the performance impact of either over provisioning address pools, or not provisioning them enough. InkBridgeDHCP suffers no performance impact in either of these scenarios, dramatically simplifying operational considerations.


InkBridgeDHCP is fully featured and supports the following IETF standards for DHCPv4.
- RFC-2131 Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
- RFC-2241 DHCP Options for Novell Directory Services
- RFC-2242 NetWare/IP Domain Name and Information
- RFC-2485 DHCP Option for The Open Group's User Authentication Protocol
- RFC-2563 DHCP Option to Disable Stateless Auto-Configuration in IPv4 Clients
- RFC-2610 DHCP Options for Service Location Protocol
- RFC-2937 The Name Service Search Option for DHCP
- RFC-3004 The User Class Option for DHCP
- RFC-3011 The IPv4 Subnet Selection Option for DHCP
- RFC-3046 DHCP Relay Agent Information Option
- RFC-3118 Authentication for DHCP Messages
- RFC-3361 Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP-for-IPv4) Option for Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) Servers
- RFC-3397 Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Domain Search Option
- RFC-3442 The Classless Static Route Option for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) version 4
- RFC-3495 Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Option for CableLabs Client Configuration
- RFC-3679 Unused Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Option Codes
- RFC-3825 Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol Option for Coordinate-based Location Configuration Information
- RFC-3925 Vendor-Identifying Vendor Options for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol version 4 (DHCPv4)
- RFC-4039 Rapid Commit Option for the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol version 4 (DHCPv4)
- RFC-4174 The IPv4 Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Option for the Internet Storage Name Service
- RFC-4280 Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Options for Broadcast and Multicast Control Servers
- RFC-4388 Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Leasequery
- RFC-4578 Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Options for the Intel Preboot eXecution Environment (PXE)
- RFC-4701 The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Client Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) Option
- RFC-4776 Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCPv4 and DHCPv6) Option for Civic Addresses Configuration Information
- RFC-4833 Timezone Options for DHCP
- RFC-5071 Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol Options Used by PXELINUX
- RFC-5192 DHCP Options for Protocol for Carrying Authentication for Network Access (PANA) Authentication Agents
- RFC-5223 Discovering Location-to-Service Translation (LoST) Servers Using the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
- RFC-5417 Control And Provisioning of Wireless Access Points (CAPWAP) Access Controller DHCP Option
- RFC-5678 Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCPv4 and DHCPv6) Options for IEEE 802.21 Mobility Services (MoS) Discovery
- RFC-5859 TFTP Server Address Option for DHCPv4
- RFC-5659 IPv6 Rapid Deployment on IPv4 Infrastructures (6rd) -- Protocol Specification
- RFC-5986 Discovering the Local Location Information Server (LIS)
- RFC-6011 Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) User Agent Configuration
- RFC-6153 DHCPv4 and DHCPv6 Options for Access Network Discovery and Selection Function (ANDSF) Discovery
- RFC-6656 Description of Cisco Systems' Subnet Allocation Option for DHCPv4
- RFC-6926 DHCPv4 Bulk Leasequery
- RFC-7291 DHCP Options for the Port Control Protocol (PCP)
- RFC-7710 Captive-Portal Identification Using DHCP or Router Advertisements (RAs)
- RFC-7839 Access-Network-Identifier Option in DHCP
- RFC-8357 Generalized UDP Source Port for DHCP Relay
- RFC-8925 IPv6-Only Preferred Option for DHCPv4
InkBridgeDHCP is fully featured and supports the following IETF standards for DHCPv6.
- RFC-3315 Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol for IPv6 (DHCPv6)
- RFC-3319 Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCPv6) Options for Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) Servers
- RFC-3633 IPv6 Prefix Options for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) version 6
- RFC-3646 DNS Configuration options for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol for IPv6 (DHCPv6)
- RFC-3898 Network Information Service (NIS) Configuration Options for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol for IPv6 (DHCPv6)
- RFC-4075 Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP) Configuration Option for DHCPv6
- RFC-4242 Information Refresh Time Option for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol for IPv6 (DHCPv6)
- RFC-4280 Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Options for Broadcast and Multicast Control Servers
- RFC-4580 Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol for IPv6 (DHCPv6) Relay Agent Subscriber-ID Option
- RFC-4649 Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol for IPv6 (DHCPv6) Relay Agent Remote-ID Option
- RFC-4704 The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol for IPv6 (DHCPv6) Client Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) Option
- RFC-4776 Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCPv4 and DHCPv6) Option for Civic Addresses Configuration Information
- RFC-4833 Timezone Options for DHCP
- RFC-4994 DHCPv6 Relay Agent Echo Request Option
- RFC-5007 DHCPv6 Leasequery
- RFC-5192 DHCP Options for Protocol for Carrying Authentication for Network Access (PANA) Authentication Agents
- RFC-5223 Discovering Location-to-Service Translation (LoST) Servers Using the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
- RFC-5417 Control And Provisioning of Wireless Access Points (CAPWAP) Access Controller DHCP Option
- RFC-5678 Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCPv4 and DHCPv6) Options for IEEE 802.21 Mobility Services (MoS) Discovery
- RFC-5908 Network Time Protocol (NTP) Server Option for DHCPv6
- RFC-5970 DHCPv6 Options for Network Boot
- RFC-5986 Discovering the Local Location Information Server (LIS)
- RFC-6011 Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) User Agent Configuration
- RFC-6153 DHCPv4 and DHCPv6 Options for Access Network Discovery and Selection Function (ANDSF) Discovery
- RFC-6225 Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol Options for Coordinate-Based Location Configuration Information
- RFC-6334 Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol for IPv6 (DHCPv6) Option for Dual-Stack Lite
- RFC-6355 Definition of the UUID-Based DHCPv6 Unique Identifier (DUID-UUID)
- RFC-6422 Relay-Supplied DHCP Options
- RFC-6440 The EAP Re-authentication Protocol (ERP) Local Domain Name DHCPv6 Option
- RFC-6603 Prefix Exclude Option for DHCPv6-based Prefix Delegation
- RFC-6607 Virtual Subnet Selection Options for DHCPv4 and DHCPv6
- RFC-6610 DHCP Options for Home Information Discovery in Mobile IPv6 (MIPv6)
- RFC-6731 Improved Recursive DNS Server Selection for Multi-Interfaced Nodes
- RFC-6784 Kerberos Options for DHCPv6
- RFC-6939 Client Link-Layer Address Option in DHCPv6
- RFC-6977 Triggering DHCPv6 Reconfiguration from Relay Agents
- RFC-7037 RADIUS Option for the DHCPv6 Relay Agent
- RFC-7078 Distributing Address Selection Policy Using DHCPv6
- RFC-7083 Modification to Default Values of SOL_MAX_RT and INF_MAX_RT'
- RFC-7341 DHCPv4-over-DHCPv6 (DHCP 4o6) Transport
- RFC-7598 DHCPv6 Options for Configuration of Softwire Address and Port-Mapped Clients
- RFC-7600 IPv4 Residual Deployment via IPv6 - A Stateless Solution (4rd)
- RFC-7653 DHCPv6 Active Leasequery
- RFC-7710 Captive-Portal Identification Using DHCP or Router Advertisements (RAs)
- RFC-7839 Access-Network-Identifier Option in DHCP
- RFC-8026 Unified IPv4-in-IPv6 Softwire Customer Premises Equipment (CPE): A DHCPv6-Based Prioritization Mechanism
- RFC-8115 DHCPv6 Option for IPv4-Embedded Multicast and Unicast IPv6 Prefixes
- RFC-8156 DHCPv6 Failover Protocol
Get InkBridgeDHCP
Find out how InkBridgeDHCP can be deployed into your ecosystem.
Focus on your business, not your network
Check out our full suite of foundational protocol products for RADIUS, DHCP, TACACS+, and DNS. Our products, coupled with world class professional services and support, ensures that your network is always fast, secure, and resilient.
Learn More
Does FreeRADIUS support DHCP?
We are happy to announce that FreeRADIUS 3 is now fully compliant with the base DHCP standards. Previous versions supported the base DORA exchange, but lacked some features such as Decline packets.
With greater flexibility and performance that is as fast or faster than the ISC DHCP server, FreeRADIUS is now a compelling option if you find yourself limited by your current implementation.
DHCP enhancement in FreeRADIUS 3
As part of our contributions to the FreeRADIUS community, InkBridge Networks took on the task of overhauling its DHCP support. The result is the same highly flexible and configurable DHCP server, but now easier to configure and outperforms both ISC and Kea DHCP in most common scenarios. And it’s available now, in FreeRADIUS 3.0.22.

Get in touch with the experts!
Whether you’re deploying an entirely new system, updating an existing one, or just need an expert review.

